Learning how to recharge a hybrid car can feel confusing, with conflicting information about whether you need to plug it in or not. You might be wondering if you need a special charger, if you can use a regular wall outlet, or if the car just handles it all on its own. The truth is, the answer depends entirely on which type of hybrid you own.
The method for recharging a hybrid car depends entirely on its type. Traditional hybrids (HEVs) automatically recharge their own batteries while you drive. Plug-in hybrids (PHEVs) have this ability but also require plugging into an external power source to maximize their electric range.
Leveraging a detailed analysis of manufacturer specifications and energy authority data, this guide clears up the confusion once and for all. We’ll break down the crucial differences between hybrid types, explain the automatic charging process for traditional hybrids, and provide a complete step-by-step guide to plugging in a PHEV. This will give you the confidence to manage your vehicle effectively and get the most out of every mile.
Key Facts
- Two Core Types: The method to recharge a hybrid car is determined by its type: a traditional hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) which is self-charging, or a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) which requires external charging.
- Regenerative Braking is Key: Both types of hybrids use regenerative braking, a process that captures the kinetic energy lost during slowing down and converts it back into electricity to charge the battery, as detailed by afdc.energy.gov.
- PHEVs Offer Electric-Only Range: Plug-in hybrids have larger batteries that provide an electric-only driving range, typically between 10 to 80 miles, which is only accessible if the vehicle is regularly charged from an external source.
- Home Charging is Simple for PHEVs: A PHEV can be fully charged overnight in 8-12 hours using a standard 120-volt household outlet, a method known as Level 1 charging, according to data from ev-lectron.com.
- Not Charging a PHEV is Inefficient: If a plug-in hybrid is never charged externally, it operates like a traditional hybrid but with the added weight of a larger battery, which can lead to worse fuel economy than a standard HEV.
First, What Type of Hybrid Do You Have? The Crucial Difference
The method for recharging a hybrid car depends entirely on its type. Traditional hybrids (HEVs) automatically recharge their own batteries while you drive. Plug-in hybrids (PHEVs) have this ability but also require plugging into an external power source to maximize their electric range. Before you can learn how to recharge your hybrid car, you must first identify which kind you have. This single distinction is the most important piece of information for any hybrid owner. A traditional Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) functions very differently from a Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) when it comes to power.

HEVs are often called “self-charging” because their small battery is replenished automatically by the gasoline engine and through a process called regenerative braking. You never need to plug them in. PHEVs, on the other hand, have a much larger battery pack that allows them to drive for a significant distance on electricity alone. To use this feature, you must plug the vehicle into an external power source.
Here’s a simple breakdown of the fundamental difference:
| Feature | Traditional Hybrid (HEV) | Plug-in Hybrid (PHEV) |
|---|---|---|
| Requires Plugging In? | No | Yes |
| Primary Power Source | Gasoline Engine & Electric Motor | Electric Motor (initially), then Gasoline Engine |
| Electric-Only Driving | Very limited (e.g., low speeds) | Yes (Typically 10-80 miles) |
| Charging Method | Self-charging only | Self-charging and External charging |
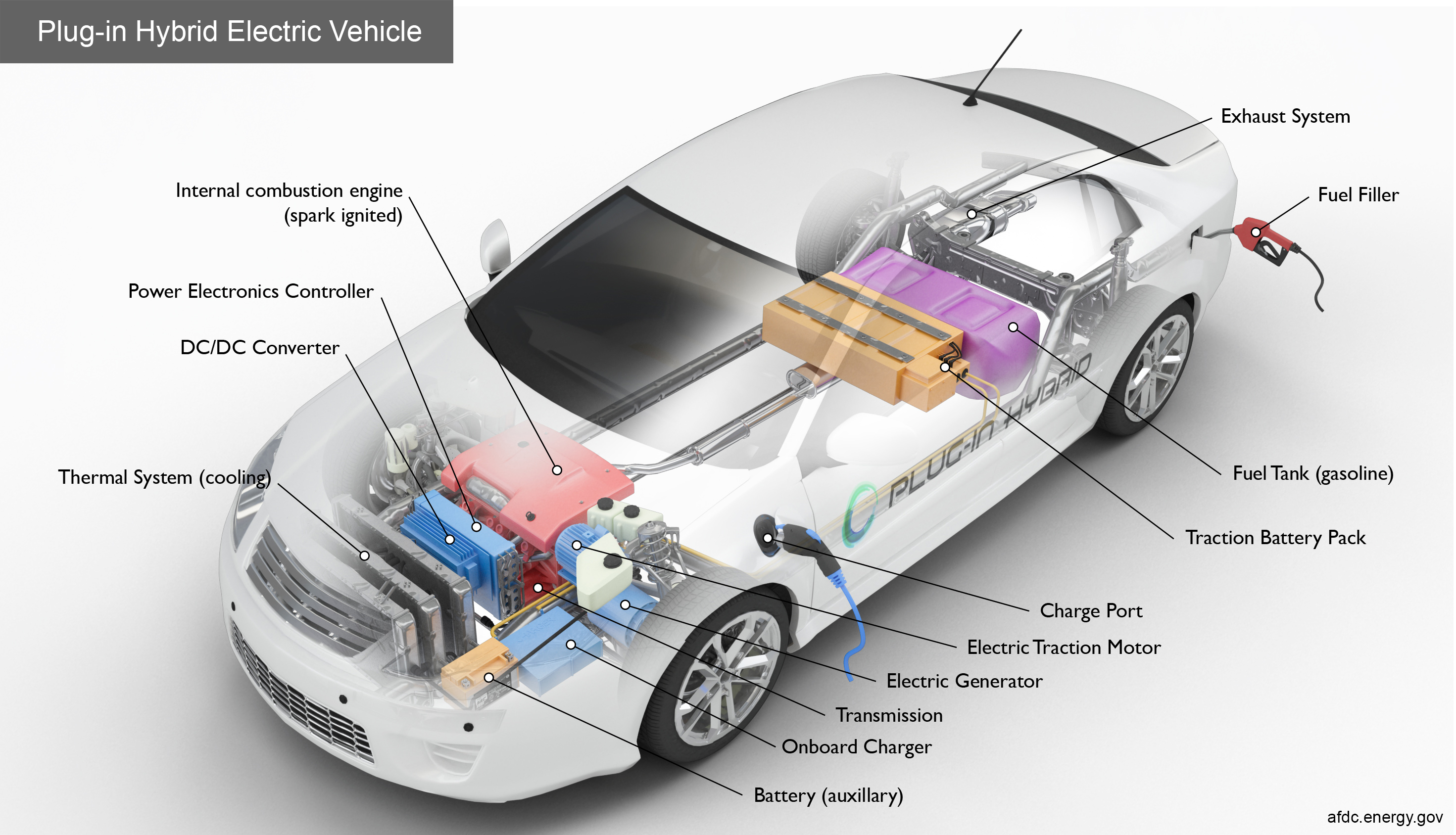
Not sure which you own? Check for a charge port on the side of your car—that’s the tell-tale sign of a plug-in hybrid.
How Traditional Hybrids (HEVs) Recharge Themselves: The “No Charger Needed” Guide
Traditional hybrids (HEVs) charge their batteries automatically in two ways: 1) through regenerative braking, which captures energy when you slow down, and 2) by using the internal combustion engine to generate electricity. No external plugging-in is required. If you own a traditional hybrid like a Toyota Prius or a standard Honda Accord Hybrid, you never have to think about how to recharge the hybrid car battery. The vehicle’s sophisticated system manages its own power needs seamlessly in the background.
The self-charging process relies on two brilliant engineering principles that work together to keep the traction battery pack topped up:
- Regenerative Braking: This is the primary method of charging. When you take your foot off the accelerator or press the brake pedal, the electric motor reverses its function. Instead of using electricity to turn the wheels, it acts like a generator. The wheels’ momentum spins the motor, creating electricity that is sent back to the battery. This process converts kinetic energy that would normally be wasted as heat in conventional brakes into usable power.
- Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) as a Generator: The gasoline engine doesn’t just power the car; it can also be used to generate electricity. The car’s computer, known as the power electronics controller, constantly monitors the battery’s charge level. If the charge drops too low, or if the engine is running in its most efficient range, it will divert some of its power to run the electric generator and send a charge to the battery.
This entire system, as explained by afdc.energy.gov, is designed for maximum efficiency without any driver intervention. The car decides when and how to charge the battery to optimize fuel economy.
Pro Tip: To maximize charging from regenerative braking, practice smooth deceleration and anticipate stops, especially in city traffic. Gentle, prolonged braking captures more energy than sudden, hard stops.
Understanding Regenerative Braking
Regenerative braking allows a hybrid to recapture energy during slowing down. The electric motor reverses its function, acting like a generator to convert motion back into electricity for the battery. This technology is the secret sauce that makes hybrid vehicles so efficient, especially in the city.
Regenerative braking is a process where a hybrid’s electric traction motor acts as a generator during braking or deceleration, converting the car’s kinetic energy back into electricity to be stored in the battery.
Instead of relying solely on friction brake pads to slow down, a hybrid uses the resistance of the electric motor to do much of the work. This has several key benefits:
- Improved Fuel Economy: By recapturing energy that would otherwise be wasted, the gasoline engine doesn’t have to work as hard to charge the battery, saving fuel. Analysis from ev-lectron.com notes this process is highly efficient in stop-and-go traffic.
- Reduced Brake Wear: Since the electric motor is doing a significant portion of the braking, the traditional brake pads and rotors last much longer, saving you money on maintenance.
Quick Fact: The energy captured by regenerative braking would otherwise be lost as heat in a conventional car’s braking system.
How to Charge a Plug-in Hybrid (PHEV): Your Complete Guide to Plugging In
To charge a plug-in hybrid (PHEV), you must connect it to an external power source using its charge port. Options range from slow overnight charging with a standard home outlet (Level 1) to rapid charging in a few hours with a dedicated 240V charger (Level 2). If you own a PHEV, like a Toyota RAV4 Prime or a Ford Escape PHEV, you get the best of both worlds: a self-charging hybrid system and a large battery you can charge for significant all-electric driving.
Regularly charging your PHEV is crucial. If you don’t, you’re essentially driving a heavier, less efficient traditional hybrid. The extra weight of the large battery pack means you’ll get worse fuel economy if you’re not taking advantage of its electric range. Learning how to recharge your hybrid car properly is key to unlocking its full potential for savings and performance.
Which charging speed would best fit your daily driving routine?
Option 1: Level 1 Charging at Home (The Easiest Method)
Use the portable charging cord that came with your PHEV and plug it into any standard, grounded 120-volt household outlet for easy, albeit slow, overnight charging. This is the simplest and most accessible way to recharge a hybrid car at home.

What You’ll Need:
* Your Plug-in Hybrid Vehicle
* The Level 1 portable charging cord that came with your car
* A standard, grounded 120-volt wall outlet (like any in your home)
Here’s the simple step-by-step process:
- Park and Turn Off: Park your vehicle in a safe location within reach of an outlet and ensure it is turned off.
- Open the Charge Port: Locate and open the charge port door on your vehicle.
- Plug Into the Wall First: For safety, plug the charger’s wall plug into the grounded 120-volt outlet before connecting it to the car.
- Connect to Your Car: Take the connector at the other end of the cord and plug it firmly into your vehicle’s charge port. You should hear a click, and an indicator light on the dashboard or charger will confirm that charging has begun.
This method is slow, typically adding 3-4 miles of range per hour and taking 8-12 hours for a full charge. However, as noted by EnergySage, for many PHEV drivers who can charge overnight, a Level 1 charger is all they really need.
Did You Know? The portable charger that came with your PHEV is a Level 1 charger. You can start using it tonight with no special installation required!
Option 2: Level 2 Charging (Faster Home & Public Charging)
For significantly faster charging (2-3 hours), use a Level 2 charger. This requires a 240-volt circuit, which can be professionally installed in your home or accessed at most public charging stations. If overnight charging isn’t fast enough for your lifestyle, upgrading to Level 2 is the best solution.
Level 2 chargers use a 240-volt connection, similar to what a household electric dryer or oven uses. This higher voltage allows them to charge a PHEV battery much faster, typically completing a full charge in just 2 to 3 hours.
Here’s a direct comparison:
| Level 1 Charging | Level 2 Charging | |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | 120-Volt (Standard Outlet) | 240-Volt (Dryer Outlet) |
| Full Charge Time | 8-12 Hours | 2-3 Hours |
| Installation | None Needed | Professional Installation Required (at home) |
| Best For | Overnight charging, low-mileage drivers | Quick top-ups, high-mileage drivers |
At Home: You can have a Level 2 charging station, often called a “wallbox,” professionally installed in your garage. This involves an electrician running a dedicated 240-volt circuit, and it’s important to note this may require upgrades to your home’s electrical panel.
In Public: Most public charging stations you find at shopping centers, workplaces, and parking garages are Level 2 chargers.
Here’s a look at the pros and cons:
* Pro: ✅ Drastically reduces charging time, offering more flexibility.
* Pro: ✅ Enables you to get a significant charge during a short stop at a public station.
* Con: ❌ Home installation involves an upfront cost for the unit and an electrician.
Consider the cost of installation versus the convenience of a 2-hour charge. Is a Level 2 charger the right investment for you?
To make your home charging setup even more efficient, investing in a high-quality Level 2 charger can significantly cut down on charging time and prepare you for future electric vehicles.
FAQs: Your Hybrid Charging Questions Answered
Can you charge any hybrid car at a public charging station?
No. Only Plug-in Hybrids (PHEVs) can be charged at a public charging station because they have a physical charge port. Traditional hybrids (HEVs) cannot be plugged in.
Do I have to charge a plug-in hybrid (PHEV)?
While a PHEV will still run on its gasoline engine if not charged, you should charge it regularly. Not charging it means you miss out on the fuel economy benefits and are carrying the extra weight of the battery, potentially making it less efficient than a standard hybrid.
Can I use a regular wall outlet to charge my hybrid?
Yes, if you have a Plug-in Hybrid (PHEV), you can use a standard 120-volt household outlet. This is called Level 1 charging and is the slowest method, typically requiring 8-12 hours for a full charge.
How do I charge my Toyota hybrid battery?
This depends on the model. A standard Toyota Prius (HEV) charges its own battery automatically while you drive. A Toyota RAV4 Prime (PHEV) must be plugged into an outlet or charging station to recharge its larger battery.
How often should you charge a plug-in hybrid car?
For maximum benefit, you should charge a plug-in hybrid (PHEV) as often as possible, ideally every night. This ensures you can use the electric-only range for your daily driving and rely less on the gasoline engine.
Key Takeaways: Your Hybrid Charging Cheat Sheet
Understanding how to recharge a hybrid car comes down to one simple question: can you plug it in? Once you know the answer, everything else falls into place. Here is a final summary of the most important points to remember.
- Identify Your Type: The first and most critical step is to determine if you have a traditional hybrid (HEV) that charges itself or a plug-in hybrid (PHEV) that needs an external power source.
- HEVs are Automatic: If you have an HEV, you don’t need to do anything. The car manages its battery charge through regenerative braking and its gasoline engine. No plugs, no chargers, no hassle.
- PHEVs Need to Be Plugged In: To get the significant fuel economy and performance benefits of a PHEV, you must charge it regularly.
- Charging Options are Flexible: PHEV owners can use a simple Level 1 charger with any standard outlet for easy overnight charging or upgrade to a faster Level 2 charger for quick top-ups at home or in public.
Now that you know exactly how to power your vehicle, you can drive with confidence and maximize your fuel savings.
Last update on 2025-12-02 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API










